When it comes to choosing plants for your home or garden, you may come across the terms "tissue culture" and "potted/bunched plants." But what do these terms mean, and how do they differ? Let's explore the differences between tissue culture plants and potted/bunched plants.

What is Tissue Culture?
Tissue culture plants are grown in a laboratory setting using a process called micropropagation. This method involves taking a small piece of plant tissue, such as a leaf or stem, and placing it in a nutrient-rich medium to encourage growth. Tissue culture allows for the rapid production of large quantities of plants with identical genetic characteristics.

What are Potted/Bunched Plants?
Potted or bunched plants, on the other hand, are grown in traditional soil-based environments. These plants are typically grown from seeds or cuttings and are nurtured in pots or bunches until they are ready for sale. Potted plants are often larger in size and may have more established root systems compared to tissue culture plants.
Key Differences
One of the main differences between tissue culture and potted/bunched plants is the method of propagation. Tissue culture plants are produced in a controlled laboratory environment, while potted/bunched plants are grown in more traditional settings. Additionally, tissue culture plants are often smaller in size and may take longer to acclimate to new environments compared to potted plants.
Another key difference is the genetic uniformity of tissue culture plants. Because tissue culture plants are produced from a single piece of plant tissue, they are genetically identical. In contrast, potted/bunched plants may exhibit genetic variation due to the use of seeds or cuttings from different parent plants.
Which is Better?
Both tissue culture and potted/bunched plants have their own advantages and disadvantages. Tissue culture plants are ideal for mass production and ensuring genetic uniformity, while potted/bunched plants may be better suited for immediate planting and faster growth. The choice between the two types of plants ultimately depends on your specific needs and preferences.
Whether you opt for tissue culture or potted/bunched plants, both can add beauty and greenery to your space. Consider the differences between the two types of plants to make an informed decision for your home or garden.
Tissue culture plants are a fascinating and innovative way to propagate plants in a controlled environment. This method involves growing plant cells or tissues in a nutrient-rich medium under sterile conditions. But how exactly does it work?

Benefits of Tissue Culture Plants
One of the main advantages of tissue culture plants is their ability to produce a large number of plants in a short amount of time. This method is also useful for propagating rare or endangered plant species, as it allows for the preservation and multiplication of these plants.

How to Care for Tissue Culture Plants
When caring for tissue culture plants, it is important to provide them with the right growing conditions, including adequate light, temperature, and humidity. It is also crucial to monitor the plants for any signs of contamination, as tissue culture plants are sensitive to pathogens.
The Future of Tissue Culture Plants
As technology continues to advance, tissue culture plants are becoming more widely used in the horticulture industry. This method offers a sustainable and efficient way to produce high-quality plants with minimal environmental impact.
In conclusion, tissue culture plants are a valuable tool for plant propagation and conservation. By understanding the principles behind tissue culture and providing the right care, gardeners and horticulturists can enjoy the benefits of these unique and innovative plants.
When it comes to tissue culture plants, there are several important factors to keep in mind to ensure their success. Whether you are a seasoned gardener or just starting out, understanding these key considerations can make a significant difference in the health and growth of your plants.

Quality of Starting Material
One of the most critical aspects of tissue culture plants is the quality of the starting material. It is essential to begin with healthy, disease-free plant tissue to avoid any issues down the line. By starting with high-quality material, you are setting your plants up for success from the very beginning.
Growth Medium and Nutrient Requirements
The growth medium and nutrient requirements for tissue culture plants are unique and must be carefully monitored. Ensuring the proper balance of nutrients and pH levels in the growth medium is crucial for the plants to thrive. By providing the right environment, you can support healthy growth and development.
Temperature and Light Conditions
Temperature and light conditions play a significant role in the growth of tissue culture plants. It is essential to maintain consistent temperature levels and provide adequate light for photosynthesis. By optimizing these conditions, you can promote optimal growth and ensure the overall health of your plants.
Contamination Control
Contamination can be a significant issue when working with tissue culture plants. It is crucial to maintain a sterile environment and follow proper sterilization protocols to prevent contamination from affecting your plants. By implementing strict contamination control measures, you can safeguard the health of your plants.
Acclimatization Process
Once your tissue culture plants have grown and developed, it is important to acclimatize them to their new environment before transplanting them. Gradually exposing the plants to external conditions can help them adjust and thrive in their new surroundings. By following a careful acclimatization process, you can ensure a successful transition for your plants.
By considering these key factors when working with tissue culture plants, you can set yourself up for success and enjoy healthy, thriving plants. With the right knowledge and attention to detail, you can cultivate a beautiful and vibrant garden filled with tissue culture plants.
Tell us - Was this article helpful? Please comment your thoughts below!
If you have any questions regarding this article, please DM us on Instagram or Facebook (@plantedpro), or email us directly at hi@plantedpro.com so we can assist you - questions cannot be replied to here.
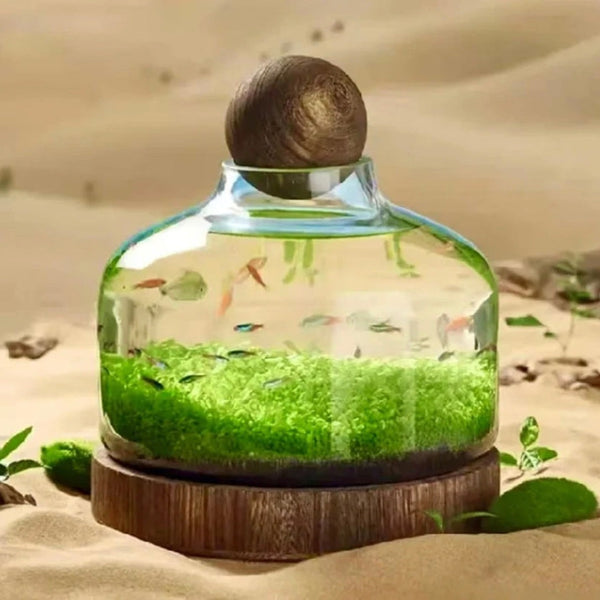
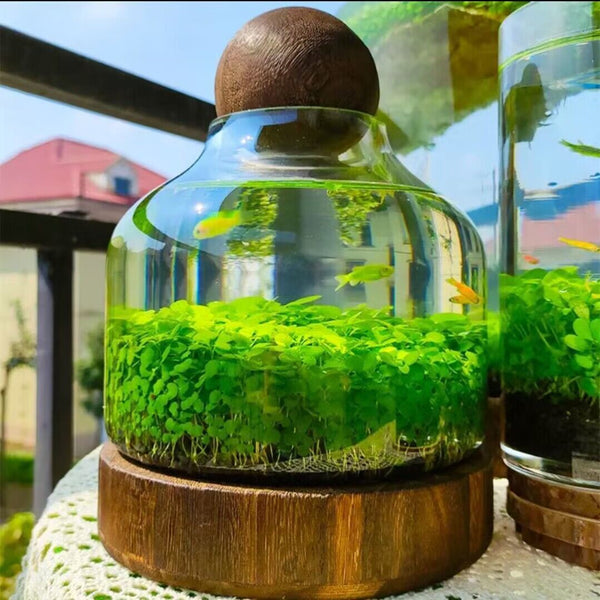
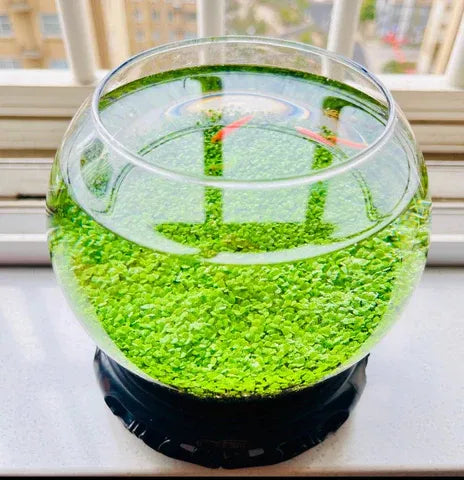
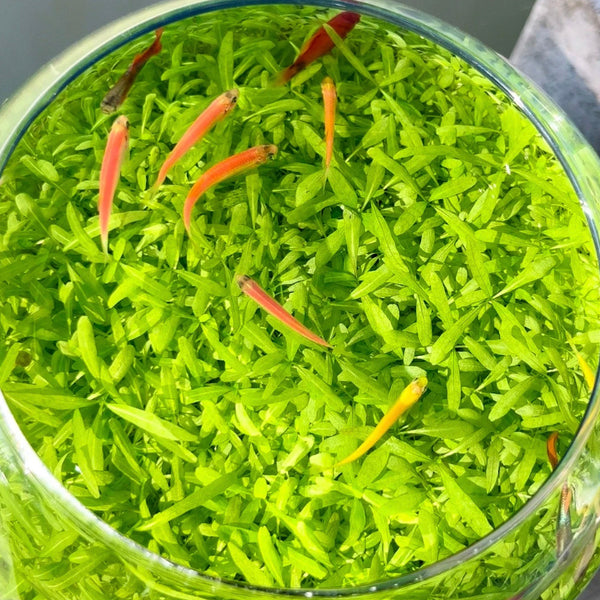








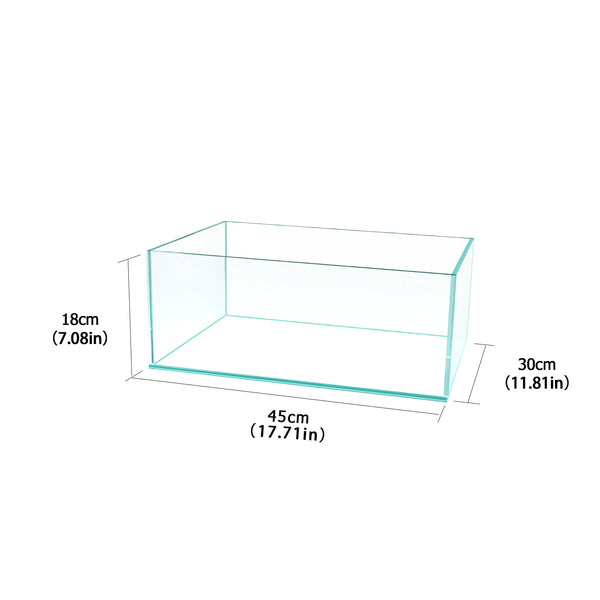

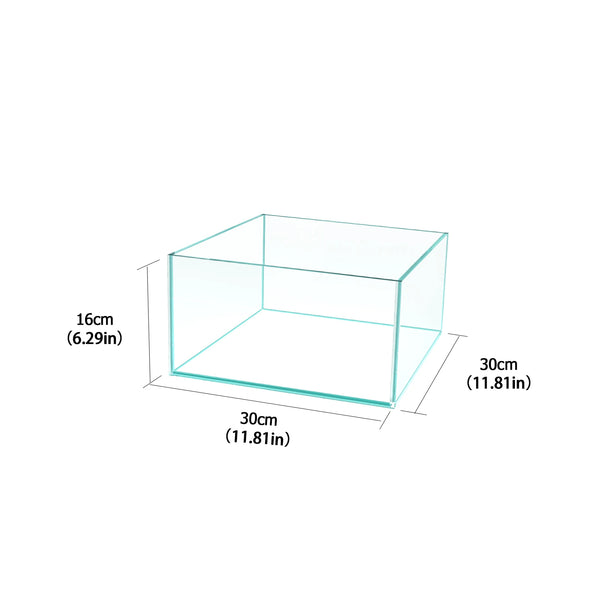

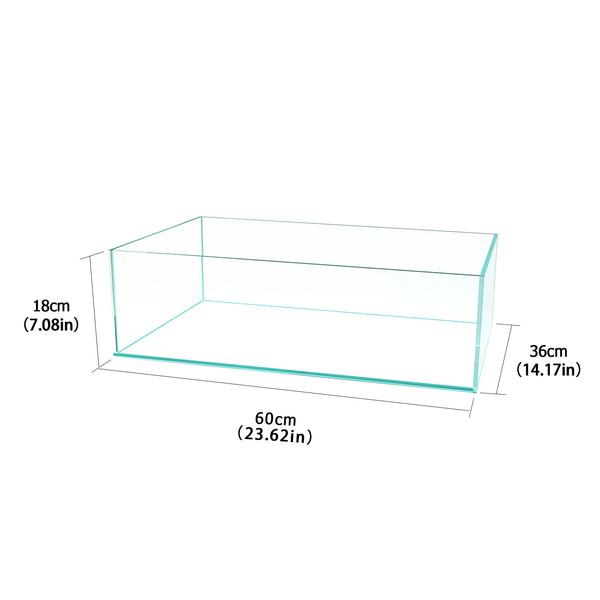

























![Pavilions Moss Microecological Landscape [Including Internal Plants + Decoration]](http://plantedpro.com/cdn/shop/files/Pavilion_Moss_Planted_Pro.png?crop=center&height=600&v=1745762480&width=600)
![Tree of Life - Moss Microlandscape [Including Internal Plants + Decoration]](http://plantedpro.com/cdn/shop/files/11_900x_e50e9d85-02a0-4773-944e-d2cd82674841.jpg?crop=center&height=600&v=1730216177&width=600)
![Green Hills - Moss Microlandscape [Including Internal Plants + Decoration]](http://plantedpro.com/cdn/shop/files/20240910013738_1080x_2859d709-be4d-4f60-a2ff-198aafae9f77.jpg?crop=center&height=600&v=1730215869&width=600)
Leave a Comment